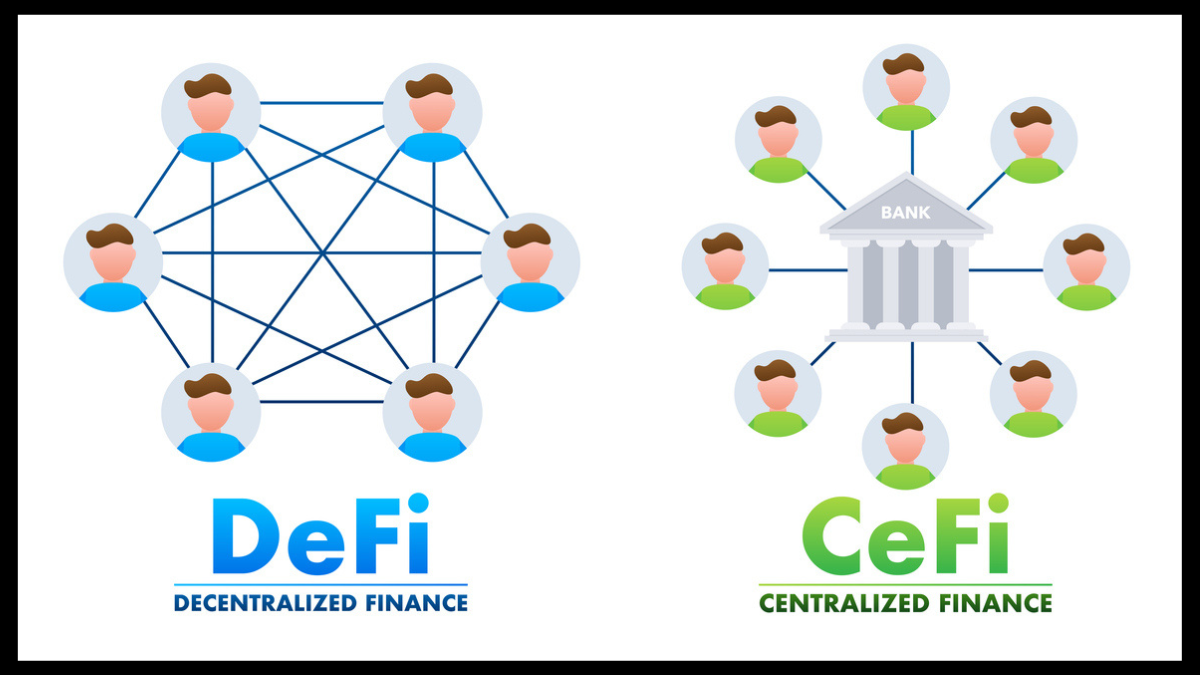
Cryptocurrency trading and transactions can follow either a centralized (CeFi) or decentralized (DeFi) approach. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each method is crucial for anyone involved in the crypto space. Follow along below as we dive deeper into the differences between CeFi and DeFi.
Historical Context of Centralized Finance
For the last century, financial operations have been predominantly centralized. Banks, regulatory authorities, and governments have overseen the provision of funding and facilitation of transactions. These centralized entities ensure the stability and regulation of financial systems, managing everything from money creation to transaction oversight.
The Emergence of Cryptocurrency
The rise of cryptocurrency has disrupted traditional financial operations. Unlike fiat currency, which is created and regulated by central governments, cryptocurrency operates independently of government control. This shift has led to the development of two primary approaches to managing crypto transactions: Centralized Finance (CeFi) and Decentralized Finance (DeFi).
What is Centralized Finance (CeFi)?
CeFi involves handling cryptocurrency transactions through centralized exchanges. These platforms function similarly to traditional stock brokerages and investment firms, managing the buying, selling, and trading of crypto assets.
Key Features of CeFi
Central Authority: A central entity oversees all operations, ensuring security, compliance, and transaction execution.
KYC and AML Compliance: Users must undergo Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) checks to verify their identity, helping to prevent illicit activities.
Custodial Services: CeFi platforms hold users’ crypto assets and private keys, taking responsibility for their security and management.
Fiat Conversion: CeFi exchanges often allow users to buy cryptocurrencies using fiat currency, making it easier for newcomers to enter the crypto market.
Cross-Chain Transactions: These platforms facilitate the exchange of different cryptocurrencies, enabling cross-chain operations.
Margin Trading and Loans: CeFi platforms can offer margin trading and direct lending services, allowing users to leverage their assets.
Advantages of CeFi
Customer Service: Users have access to customer support for assistance.
Fiat Integration: Easy conversion between fiat and cryptocurrencies.
Cross-Chain Support: Facilitates trading across different crypto tokens.
Margin Trading: Enables trading with borrowed funds.
Income Opportunities: Users can earn interest on their crypto assets.
Disadvantages of CeFi
Custody Risks: Users’ funds are held by the platform, not directly controlled by the user.
Regulatory Risks: Compliance with varying regulatory requirements can pose risks.
Centralized Control: Reliance on the central authority for transaction execution and asset security.
Examples of CeFi Platforms
- Binance
- Coinbase
- Gemini
- Kraken
- Nexo
- Helio Lending
What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
DeFi uses blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer cryptocurrency transactions without the need for a central authority. Instead of relying on centralized exchanges, DeFi leverages smart contracts to automate and manage transactions.
Key Features of DeFi
Decentralized Control: Users retain control over their assets and private keys.
Smart Contracts: Automated contracts execute transactions based on predefined rules, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
Permissionless Systems: No need for third-party verification; anyone can participate.
DApps: Decentralized applications (dApps) run on blockchain networks to facilitate various financial services.
Lower Fees: Reduced transaction fees due to the absence of central intermediaries.
Advantages of DeFi
User Custody: Users maintain control over their funds.
Permissionless Access: No barriers to entry, allowing broad participation.
Anonymity: Users can engage in transactions without revealing their identity.
Innovation: Supports the development of new financial applications and services.
Cost Efficiency: Generally lower fees compared to CeFi.
Disadvantages of DeFi
Complexity: Requires understanding of sophisticated technology and smart contracts.
Security Risks: DeFi platforms are frequent targets for cyberattacks.
Volatility: High market volatility can pose risks.
Lack of Customer Support: Automated systems lack human customer service.
Examples of DeFi Platforms
- 1inch Network
- MakerDAO
- PancakeSwap
- Stargate Finance
- Uniswap
Similarities Between CeFi and DeFi
Despite their differences, CeFi and DeFi share some common ground. Both rely on blockchain technology to provide financial services, enabling users to buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies. Additionally, both approaches aim to promote the use and adoption of cryptocurrency.
Security and Regulation
Security is a critical concern for both CeFi and DeFi. While CeFi platforms can implement centralized security measures and comply with regulations, DeFi relies on the robustness of smart contracts and decentralized protocols, which can be more vulnerable to attacks. However, CeFi platforms are not immune to security breaches either.
The Future of Finance: CeFi and DeFi
The ongoing evolution of both CeFi and DeFi indicates a future where traditional and innovative financial systems coexist. CeFi provides a familiar and regulated entry point for new users, while DeFi offers a decentralized and potentially more inclusive financial ecosystem. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each approach is essential for anyone looking to navigate the dynamic world of cryptocurrency finance.